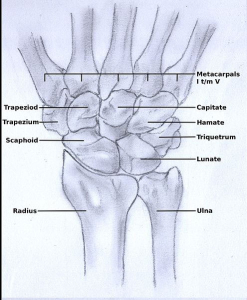
 The human wrist contains eight small carpal bones arranged in two rows of four bones each. This arrangement comprises the carpus which articulates with the two long bones of the wrist proximally, the radius and ulna, and the five metacarpals of the hand distally. Each of these bone articulations is covered by cartilage, forming several individual joints just within the wrist. The carpus is slightly concave on the palmar side of the wrist, which forms the carpal tunnel.
The human wrist contains eight small carpal bones arranged in two rows of four bones each. This arrangement comprises the carpus which articulates with the two long bones of the wrist proximally, the radius and ulna, and the five metacarpals of the hand distally. Each of these bone articulations is covered by cartilage, forming several individual joints just within the wrist. The carpus is slightly concave on the palmar side of the wrist, which forms the carpal tunnel.
The carpal tunnel houses the flexor tendons and median nerve. The radial and ulnar nerves each run on the outside of the tunnel. The extensor tendons run along the dorsal (or back) of the hand. There is a nice housing mechanism of six separate extensor compartments on the back of the hand called the extensor retinculum that houses all of the extensor tendons. Several muscles in the hand connect from these tendons to allow intricate movement in the hand and wrist.
There is also a multifaceted network of ligaments that connect the radius and ulna to the carpal and metacarpal bones. The TFCC, or Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex, is a complex of ligaments and discus that bears a substantial load of forces across the wrist, protects the articular surfaces of the wrist and stabilizes the DRUJ, Distal Radial Ulnar Joint.
As you can see, the wrist is comprised of an extremely complex network of bone articulations, ligaments, tendons, muscles and nerves, which is one of the many reasons why the wrist should be treated by a specialist.


